Bipolar disorder, previously manic-depressive illness, involves drastic mood, energy, and activity changes, affecting millions globally and straining daily life and relationships. Early recognition of its signs is vital for timely intervention and effective management, ensuring improved outcomes and well-being.
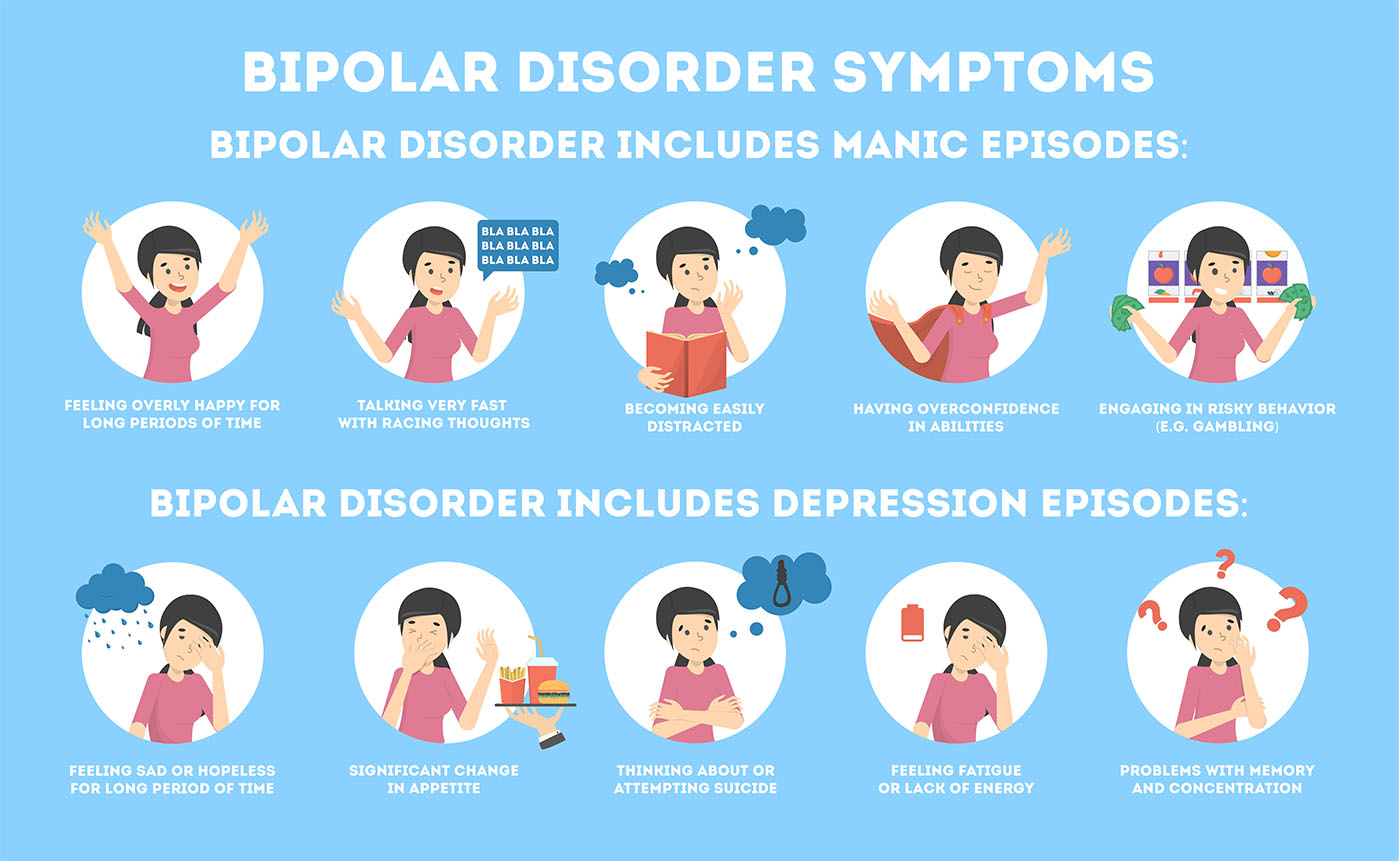
1. Mood Swings: One of the hallmark features of bipolar disorder is the presence of distinct episodes of mood swings. These swings can range from the highs of mania or hypomania to the lows of depression. During manic episodes, individuals may experience heightened energy levels, euphoria, racing thoughts, impulsivity, and a decreased need for sleep. On the other hand, depressive episodes are marked by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, fatigue, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and thoughts of death or suicide.
2. Cyclic Nature: Bipolar disorder typically follows a cyclic pattern, with periods of mania or hypomania alternating with periods of depression. These episodes can last for days, weeks, or even months, and the frequency and intensity of episodes vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience rapid cycling, characterized by four or more mood episodes within a year, while others may have more extended periods of stability between episodes.
3. Impaired Functioning: The extreme mood swings associated with bipolar disorder can significantly impair functioning in various areas of life. During manic episodes, individuals may engage in reckless behavior, such as excessive spending, risky sexual encounters, or substance abuse, which can lead to financial, legal, or interpersonal problems. Conversely, depressive episodes can make it challenging to concentrate, make decisions, or perform daily tasks, affecting work, school, and relationships.
4. Psychosocial Impact: Bipolar disorder not only affects the individual but also has a profound impact on their family, friends, and caregivers. Family members may struggle to understand the erratic behavior and mood fluctuations, leading to conflicts and strained relationships. Moreover, the stigma surrounding mental illness can contribute to feelings of shame, isolation, and reluctance to seek help, further exacerbating the psychosocial burden of the disorder.
5. Comorbid Conditions: Individuals with bipolar disorder often experience other psychiatric comorbidities, such as anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or eating disorders. These co-occurring conditions can complicate diagnosis and treatment, requiring a comprehensive approach that addresses both bipolar symptoms and any accompanying mental health issues.
6. Risk Factors: While the exact cause of bipolar disorder remains unknown, several factors may increase the risk of developing the condition. These include genetic predisposition, environmental stressors, neurotransmitter imbalances, and alterations in brain structure and function. Additionally, traumatic life events, such as childhood abuse or neglect, can contribute to the onset or exacerbation of bipolar symptoms.
7. Treatment Options: Bipolar disorder is a chronic illness that requires lifelong management, but with proper treatment, many individuals can lead fulfilling and productive lives. Treatment typically involves a combination of medication, such as mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, or antidepressants, and psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychoeducation, and interpersonal therapy. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, healthy diet, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques, can also complement medical and psychological interventions.
8. Importance of Early Intervention: Early detection and intervention are essential for improving outcomes and preventing long-term complications of bipolar disorder. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking professional help, and adhering to a tailored treatment plan are critical steps in managing the condition effectively. Education, support, and advocacy play crucial roles in reducing stigma, increasing awareness, and promoting mental health literacy within communities.
In conclusion, bipolar disorder is a complex and challenging mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings, impaired functioning, and significant psychosocial impact. By understanding the signs and symptoms, addressing risk factors, and implementing comp




